An n x n matrix (i.e., a vector of length n*n), stored row-wise: that is, A(i,j) = A[ij], where ij = i*n + j. More...
#include </home/werner/origo/vish/ocean/eagle/QuadraticMatrix.hpp>
Public Types
- typedef Matrix< N, N, Value > Base_t
-
typedef FixedArray< int, N > PermutationVector_t
- Type of the permutation vector that is required for the functions GaussDecompose() and GaussSolve().
- Type of the permutation vector that is required for the functions GaussDecompose() and GaussSolve().
- typedef Value value_type
Public Member Functions
- bool GaussDecompose (FixedArray< int, N > &perm, double EPSWEIGHT=1E-3)
- void GaussSolve (const PermutationVector_t &perm, const Column< N, value > &b, Column< N, value > &x) const
-
value maxoffd () const
- Return maximum off-diagonal element of n by n square matrix A.
- Return maximum off-diagonal element of n by n square matrix A.
- template<class OutputValue > Quadratic< N, OutputValue > operator() (const Quadratic< N, OutputValue > &A) const
- template<class OutputValue > LowerTriangular< N, OutputValue > operator() (const LowerTriangular< N, OutputValue > &A) const
- Quadratic & operator= (const LowerTriangular< N, value > &)
-
Quadratic ()
- Default constructor.
- Default constructor.
-
Quadratic (const Matrix< N, N, value > &A)
- Construct quadratic matrix from base class.
- Construct quadratic matrix from base class.
-
template<int C, class ValueA , class ValueB > Quadratic (const Matrix< N, C, ValueA > &A, const Matrix< C, N, ValueB > &B)
- Construct quadratic matrix from multiplication for two fitting non-quadratic matrices.
- Construct quadratic matrix from multiplication for two fitting non-quadratic matrices.
- Quadratic (Quadratic &, const TransposeOperation &)
-
Quadratic (const LowerTriangular< N, value > &)
- Construct a quadratic matrix from a lower triangular matrix.
- Construct a quadratic matrix from a lower triangular matrix.
Detailed Description
An n x n matrix (i.e., a vector of length n*n), stored row-wise: that is, A(i,j) = A[ij], where ij = i*n + j.
- See also:
- Matrix
- Examples:
Member Function Documentation
| bool Eagle::Quadratic::GaussDecompose | ( | FixedArray< int, N > & | perm, |
| double | EPSWEIGHT = 1E-3 |
||
| ) | [inline] |
Perform gauss decomposition of the matrix, which can and should be used instead of computing the inverse of a matrix.
The permutation operations during the composition is stored in the perm parameter, which then needs to be provided to the GaussSolve() routine.
- Note:
- The original matrix is destroyed during this operation.
- Parameters:
-
EPSWEIGHT square root of the absolut precision of the computation
| void Eagle::Quadratic::GaussSolve | ( | const PermutationVector_t & | perm, |
| const Column< N, value > & | b, | ||
| Column< N, value > & | x | ||
| ) | const [inline] |
Instead of inverting a matrix, solve a linear system of equations 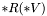 by forward and backward elimination.
by forward and backward elimination.
- Parameters:
-
perm A permutation vector as computed by GaussDecompose() b The right-hand side of the equation x On return, will contain the solution.
Eagle::Quadratic<3, double> A;
Eagle::Column<3, double> b;
Eagle::Column<3, double> x;
Eagle::FixedArray<int, 3> perm;
A = 2.5, 3.0, 1.1,
0.2, 0.1, 2.1,
0.12, 1.0, 0.3;
b = 39.0, 1.0, 34.33;
A.GaussDecompose(perm);
A.GaussSolve(perm, b, x);
The result in x then is < 16.809817, -24.730900, 16.013638 >.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- ocean/eagle/QuadraticMatrix.hpp
 1.7.5
1.7.5